Vitamin D deficiency is increasingly common, with an estimated 1 billion people worldwide having low levels. This deficiency can cause an array of symptoms and increase the risk of serious health conditions like osteoporosis, heart disease, cancer, and autoimmune disorders. Fortunately, there are several treatment options available to correct vitamin D deficiency, including oral supplements, dietary changes, sun exposure, and IV therapy. This article provides an in-depth look at using intravenous (IV) vitamin D injections to treat deficiency.
Causes of Vitamin D Deficiency
There are a few key reasons someone may become deficient in vitamin D:
-
Limited sun exposure – Our bodies produce vitamin D when our skin is exposed to sunlight. People who live in cold climates or have minimal outdoor time can easily become deficient.
-
Inadequate dietary intake – Very few foods naturally contain vitamin D, making it hard to get enough from diet alone. Fatty fish, fish liver oil, and fortified foods are among the few good food sources.
-
Malabsorption issues – Certain gastrointestinal conditions like celiac disease, Crohn’s disease, and cystic fibrosis can impair vitamin D absorption.
-
Obesity – Individuals with a BMI over 30 have lower vitamin D levels, partly due to the vitamin becoming deposited in body fat.
-
Certain medications – Some drugs like orlistat and cholestyramine can negatively interact with vitamin D absorption.
Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency
Some common symptoms of vitamin D deficiency include:
-
Fatigue and weakness
-
Bone and back pain
-
Depression
-
Impaired wound healing
-
Bone loss (osteopenia/osteoporosis)
-
Hair loss
-
Muscle pain
Health Risks Associated with Vitamin D Deficiency
If left untreated, vitamin D deficiency can lead to some serious health consequences:
-
Osteoporosis – Low bone mineral density raises fracture risk.
-
Cardiovascular disease – Vitamin D helps regulate blood pressure and heart health. Deficiency increases risk of heart attack, stroke, etc.
-
Cancer – Vitamin D plays a role in cell growth and immune function. Deficiency may raise risks of colon, breast and prostate cancers.
-
Autoimmune diseases – Vitamin D helps regulate immune function. Deficiency makes you more prone to issues like multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus.
-
Cognitive impairment – Older adults with vitamin D deficiency are at higher risk of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.
Treatment Options for Vitamin D Deficiency
If you’ve been diagnosed with a vitamin D deficiency, there are a few ways you can raise your levels again:
Oral Vitamin D Supplements
Vitamin D supplements taken by mouth are often the first line treatment. The two main forms are:
-
Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) – Derived from plants, less potent than D3.
-
Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) – Derived from animal sources, most active form.
The recommended daily dose can range from 1,000 to 10,000 IU depending on your individual needs. Supplements are affordable and accessible but can take several months to resolve deficiency. Those with absorption issues may not respond well to oral vitamin D.
Increased Sun Exposure
Spending more time outdoors allows your body to synthesize more vitamin D naturally. To raise levels, aim for:
-
5-30 minutes of midday sun 2-3 times per week.
-
Expose large areas of skin (arms, legs, back).
-
Use sunscreen after initial 5-10 minutes.
This approach is free and effective but limited for people living in cold or overcast climates. It can be difficult to get enough sun exposure year-round.
Dietary Changes
Eating more vitamin D-rich foods can help improve levels. The best dietary sources include:
-
Fatty fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel)
-
Fish liver oils
-
Fortified milk, yogurt, orange juice
-
Beef liver
-
Cheese
-
Egg yolks
However, it is difficult to consume enough vitamin D from food alone. Dietary changes work best as a complement to other approaches. Those with digestive issues absorb less vitamin D from foods.
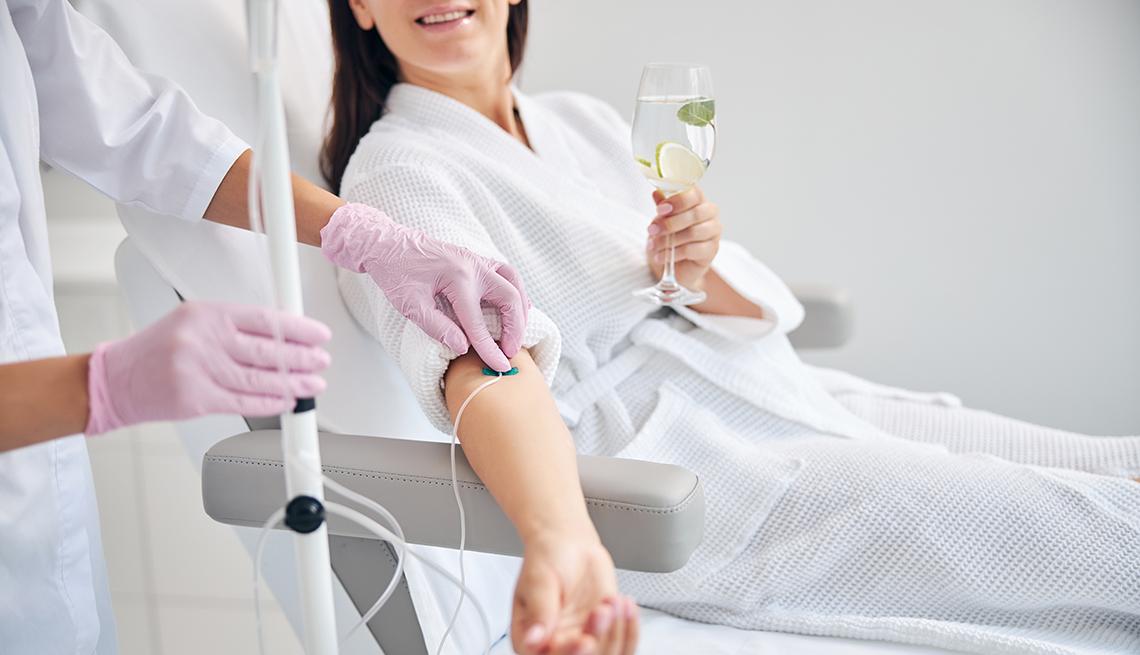
IV Vitamin D Drips
Getting intravenous (IV) injections of vitamin D allows for higher blood concentration levels to be achieved rapidly. With IV delivery, large doses of vitamin D can be administered directly into the bloodstream, bypassing digestion completely. This makes it an appealing option for those with malabsorption conditions. IV drip therapy provides a fast and effective way to correct vitamin D deficiency.
Compared to oral vitamins that build up gradually, IV vitamin D takes effect right away to replenish levels. Some key advantages of IV vitamin D include:
-
Much higher dosage possible
-
Immediate absorption into blood
-
Rapid resolution of deficiency
-
Useful for those with absorption issues
The main downsides are the inconvenience of IV administration and higher costs compared to oral supplements. However, the rapid results make it worthwhile for many deficient patients.
The Benefits of IV Vitamin D Injections
Here is a more in-depth look at the benefits provided by IV vitamin D therapy:
-
Higher blood concentration – IV allows up to 600,000 IU to be administered at once, resulting in markedly higher vitamin D levels compared to other routes.
-
Bypasses digestion – Intravenous injection sends vitamin D straight into the bloodstream, avoiding potential absorption issues in the gastrointestinal tract.
-
Rapid relief of deficiency symptoms – Patients report fast improvements in fatigue, aches and pains, low mood, and other issues after starting IV vitamin D.
-
Useful for those with absorption issues – People with digestive disorders like celiac, IBS, gastritis, SIBO, cystic fibrosis, etc. can effectively raise their vitamin D levels with IV therapy.
Overall, IV vitamin D provides a fast-acting method to reverse deficiency, especially for those who don’t respond to oral treatment. Patients often report feeling markedly better within days after their first IV vitamin D session.
What to Expect from an IV Vitamin D Treatment
Here is an overview of what an IV vitamin D session is like:
-
After checking in, you will be set up in a comfortable chair or bed.
-
The skin over your arm will be cleaned.
-
A small catheter will be inserted into your vein. This is a quick pinch and discomfort is minimal.
-
Vitamin D mixed with saline solution is then infused through the IV catheter.
-
Sessions typically last 15-30 minutes depending on the dosage given.
-
Treatment is repeated weekly or bi-weekly until levels normalize. Most people require 4-8 sessions.
-
Possible side effects include temporary flushing, low blood pressure, metallic taste, and vein irritation. Serious reactions are very rare.
IV vitamin D therapy is a straightforward, low-risk procedure when performed by qualified professionals. The infusion is well-tolerated and often described as very relaxing.
Finding a Provider of IV Vitamin D Therapy
IV vitamin D treatments are offered by:
-
Medical clinics – Some doctors, naturopaths, chiropractors, and health clinics provide IV vitamin therapy services.
-
Mobile iv drips services – Companies that come to your home or office to administer IV treatments. This offers convenience without visiting a clinic.
When choosing a provider, check for proper accreditation, licensed medical supervision, and protocols for vitamin D dosing/safety. Reputable providers will customize the IV dose based on your deficiency lab work rather than a one-size-fits-all approach. Most sessions range from $100-300 per visit depending on these factors.
Conclusion
Vitamin D deficiency is a common issue that can negatively impact your health in many ways. IV vitamin D provides a fast-acting treatment approach that bypasses absorption issues. It allows much higher doses compared to supplements or sunlight alone. IV therapy can help quickly reverse deficiency symptoms and minimize the risks of long-term health consequences. If you have very low vitamin D levels, particularly with signs of malabsorption, exploring IV treatment makes sense. Just be sure to use a qualified medical provider to ensure safety and proper dosing. With IV vitamin D you can raise your levels into the optimal range again promptly and efficiently.
FAQ
How long does it take for IV vitamin D to work?
Most patients report feeling noticeable effects within 24-48 hours after their first IV vitamin D session. Maximum benefits are typically seen after completing a series of 4-8 treatments given weekly or bi-weekly.
How often should you get IV vitamin D?
Most providers recommend IV vitamin D 1-2 times per week initially. Once levels are normalized, less frequent maintenance treatments may be advised, such as once a month.
Is IV better than taking vitamin D supplements?
IV is advantageous for those unable to raise their vitamin D adequately through supplements or sunlight alone. IV provides more rapid effects at much higher doses. However, supplements do work for most people given enough time.