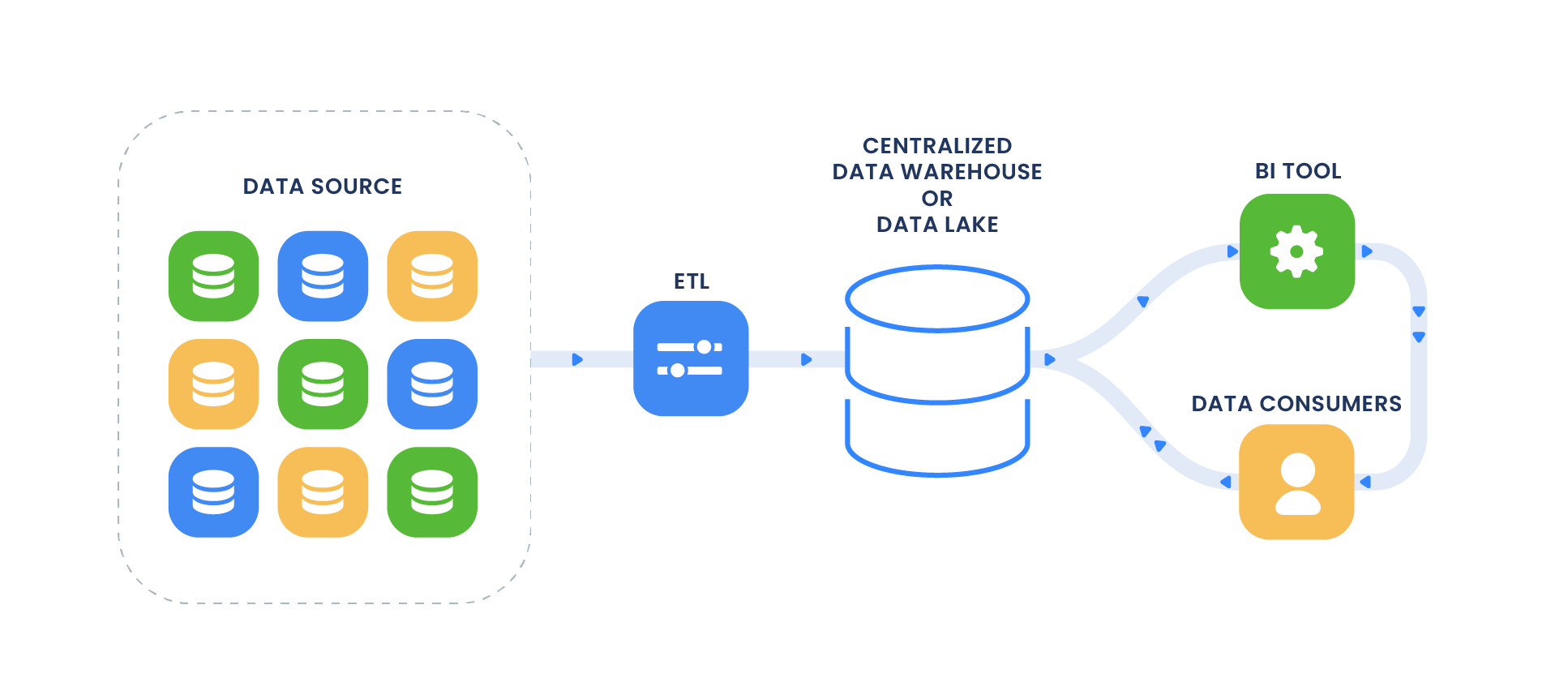
Safeguarding the Foundation: Data Security and Compliance in Data Consolidation
In the era of digital transformation, where data is a prized asset, the consolidation of diverse data sources brings both tremendous opportunities and significant responsibilities. As businesses strive to centralize their data for enhanced decision-making, the critical aspects of data security and compliance take center stage. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the importance of prioritizing data security and compliance in the context of data consolidation and explore effective strategies for safeguarding the foundation of organizational data.
1. Data Encryption as the First Line of Defense:
Data consolidation often involves the aggregation of sensitive information from various sources. To safeguard this treasure trove of data, encryption becomes paramount. Implementing robust encryption mechanisms, both in transit and at rest, ensures that even if unauthorized access occurs, the data remains unreadable and protected.
2. Access Controls and Authentication Measures:
Granular access controls and multi-factor authentication play a crucial role in fortifying the security perimeter of consolidated data. By restricting access based on roles and responsibilities, organizations can prevent unauthorized users from compromising the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive information.
3. Regular Audits and Monitoring:
Continuous monitoring and regular audits are essential components of a comprehensive data security strategy. These practices help identify unusual activities, potential security breaches, or compliance violations. By staying vigilant and proactive, organizations can swiftly respond to security incidents and maintain the trustworthiness of their consolidated data. If you are looking for Data Consolidation services and Data Consolidation Tools services then probyto is the best company in the market.
4. Data Residency and Jurisdiction Compliance:
Data consolidation often involves data transfer and storage across different geographic locations. Navigating the complexities of data residency and jurisdictional compliance is crucial to meet regulatory requirements. Understanding where data can legally reside and ensuring compliance with regional data protection laws are fundamental steps in the consolidation process.
5. Privacy-by-Design Principles:
Embedding privacy considerations into the very fabric of data consolidation is a key concept known as privacy by design. This approach involves integrating privacy measures from the outset of the consolidation project, ensuring that data protection is not an afterthought but an integral part of the entire process.
6. Regular Training on Data Security Protocols:
Human error remains a significant factor in data security breaches. Regular training programs on data security protocols, best practices, and the potential risks associated with mishandling data are crucial. Employees must be aware of their role in maintaining data security and be equipped with the knowledge to mitigate potential threats.
7. Collaboration with Legal and Compliance Teams:
A successful data consolidation strategy involves close collaboration between IT teams and legal/compliance experts. This partnership ensures that the consolidation process aligns seamlessly with regulatory requirements, reducing the risk of non-compliance and associated penalties.
Conclusion:
In the pursuit of unlocking the full potential of consolidated data, organizations must recognize that security and compliance are not mere checkboxes but foundational elements of the process. As businesses navigate the intricacies of data consolidation, a robust and proactive approach to data security and compliance is not just a legal necessity—it’s a strategic imperative. By safeguarding the foundation of their consolidated data, organizations build a resilient and trustworthy platform that can propel them forward in an era where data integrity and compliance are non-negotiable.