A photoinitiator is a molecule that, upon exposure to radiation, introduces reactive species such as cations, free radicals, and anions. These species initiate the polymerization procedure by integrating themselves into the monomer or oligomer. Photoinitiators are commonly employed in conjunction with cross-linkable monomers and oligomers, especially in UV-curable inks, adhesives, coatings, and different other products. There are two primary classes of photoinitiators: radical photoinitiators, and cationic photoinitiators.
Radical photoinitiators exhibit different reactions under UV irradiation, leading to their classification as Norrish Type I and Norrish Type II photoinitiators reliant on their precise reactions. This classification plays a crucial role in determining their functionality in different applications.
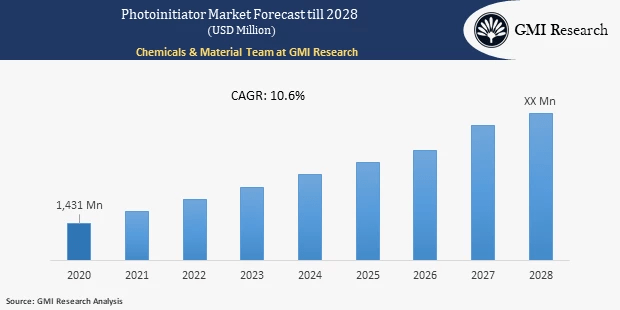
Market Drivers
The expanding automation market is predicted to propel the need for coatings and adhesives, consequently propelling an increased requirement for photoinitiators. This increase in need is further driven by the precise customization trends and the burgeoning 3D printing market. The growth of the 3D printing sector, coupled with the increasing adoption of photoinitiators within this domain, presents lucrative opportunities for vendors in the photoinitiators market. Beyond this, photoinitiators find applications in different industries, including packaging and dental products, indicating a different and expanding market. The widening usage of photoinitiators is predicted to be a significant factor in driving the global photoinitiator market forward.
In the market, photoinitiators serve as substitutes for volatile organic, compounds. Unlike VOCs, which are complex and pose difficulties for easy breakdown, photoinitiators offer a safer alternative. VOCs can lead to severe health problems if ingested directly and present environmental concerns as they are insoluble in water, lingering if not disposed of properly. The environmental and health threats linked with VOCs have promoted producers to opt for photoinitiators, addressing both safety and environmental sustainability in their procedures. This move towards utilizing photoinitiators reflects a conscientious choice by industries to mitigate potential health hazards and decrease their environmental impact.
Photoinitiators exhibit water solubility in the existence of oligomers and monomers, resulting in minimal to no environmental impact. These characteristics contribute to significant environmental benefits when photoinitiators are used in the production of coatings, adhesives, and inks. The positive environmental impact linked with the usage of photoinitiators aligns with the increasing emphasis on sustainable practices and eco-friendly alternatives in different industries. This environmentally conscious approach is predicted to further foster the global photoinitiator market, as businesses progressively prioritize solutions that not only meet their functional requirements but also contribute to wider environmental sustainability goals.
Regional Segmentation
The Asia Pacific region presently holds the leading market position and is predicted to witness accelerated growth rates in the forecast period. The significant driver for the photoinitiators market in the APAC region is the burgeoning number of electronics, automotive, and packaging industries The region benefits from less stringent rules and regulations concerning chemical handling necessary for photoinitiator synthesis, contributing to a positive impact on the market. This favorable regulatory environment, coupled with the thriving industrial segments, positions the APAC region as a foremost player in the global photoinitiator market, with predictions of sustained growth in the coming forecast period.